time.h 头文件 是 C 语言中 有关 时间的函数所储存的头文件
#include <time.h> 在介绍时间函数用法之前,我们首先要了解在 time.h 头文件中已经声明了的一个结构: struct tm
该结构在time.h 头文件内声明如下:
#ifndef _TM_DEFINED #define _TM_DEFINED struct tm { int tm_sec; int tm_min; int tm_hour; int tm_mday; int tm_mon; int tm_year; int tm_wday; int tm_yday; int tm_isdst; }; #endif 该结构内个成员所代表的意思:
struct tm { int tm_sec; //秒(0~61) int tm_min; //分(0~59) int tm_hour; //小时(0~23) int tm_mday; //日(1~31) int tm_mon; //月份(0~11) int tm_year; //年,从1970年至今经过的年数 int tm_wday; // 星期:(0~6) int tm_yday; // 天数(0~365) int tm_isdst; //夏令时 daylight-saving time } 下面来介绍几种时间函数的用法:
//函数名称: time(); //函数原型: time_t __cdecl time(time_t *_Time) { return _time64(_Time); } //函数功能:得到机器的日历时间或设置日历时间 //函数返回机器日历时间 //用法: 参数说明: timer = NULL 时得到机器日历时间, timer = 时间数值值,用于设置日历时间, time_t 是一个long 类型 #include <stdio.h> #include <time.h> int main(void) { time_t timer; timer = time(NULL); printf("%ldn", timer); } 运行结果是 秒数: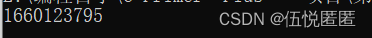
将这个秒数通过时间戳在线转换网站转换为年月日,转换网址为: https://tool.lu/timestamp/ 转换结果如下

//函数名称: localtime(); //函数原型: struct tm *__cdecl localtime(const time_t *_Time) { return _localtime32(_Time); } //函数功能: 返回一个以 tm结构表达的机器时间信息 //函数返回:以 tm 结构表达的时间 //用法: #include <stdio.h> #include <time.h> int main(void) { time_t timer; struct tm *tblock; timer = time(NULL); tblock = localtime(&timer); printf("当地时间是 %s", tblock); } 直接使用 tblock的值 输出结果是有问题的:

想要获取日常使用的时间格式 要多使用一个函数:
//函数名称: asctime(); //函数原型: char *__cdecl asctime(const struct tm *_Tm) //函数功能:获取机器时间(日期时间转换成ASCII码) //函数返回:返回的时间字符串格式为: 星期,月,日,小时:分:秒,年 //用法: #include <stdio.h> #include <time.h> int main(void) { time_t timer; struct tm *tblock; timer = time(NULL); tblock = localtime(&timer); printf("当地时间是 %s", asctime(tblock)); } //另一种用法: //结合 struct tm 结构 #include <stdio.h> #include <time.h> #include <string.h> int main(void) { struct tm t; char str[80]; t.tm_sec = 1; t.tm_min = 3; t.tm_hour = 7; t.tm_mday = 22; t.tm_mon = 11; t.tm_year = 56; t.tm_wday = 4; t.tm_yday = 0; t.tm_isdst = 0; strcpy(str, asctime(&t)); printf("%s", str); } 运行结果:
用法1:
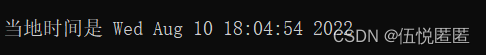
用法2:

同样使用 时间格式输出时间的还有:
//函数名称: ctime(); //函数原型: char *__cdecl ctime(const time_t *_Time) { return _ctime64(_Time); } //函数功能:得到日历时间 //函数返回:返回字符串格式: 星期,月,日,小时:分:秒,年 //用法: #include <stdio.h> #include <time.h> int main(void) { time_t t; time(&t); printf("当地时间是 %s", ctime(&t)); } 运行结果:

两次机器时间差的获取方法:
//函数名称: difftime(); //函数原型:double __cdecl difftime(time_t _Time1,time_t _Time2) //函数功能:得到两次机器时间差,单位为秒 //函数返回:时间差,单位为秒 //用法: //参数说明: time1 - 机器时间一, time2 - 机器时间二,该参数应使用 time函数获得 #include <stdio.h> #include <time.h> #include <windows.h> int main(void) { time_t first, second; first = time(NULL); Sleep(2000); second = time(NULL); printf("两者之间差了 %f 秒", difftime(second, first)); } 运行结果:

另一个 结构 时间信息 函数:
//函数名称: gmtime(); //函数原型:struct tm *__cdecl gmtime(const time_t *_Time) { return _gmtime64(_Time); } //函数功能:得到以结构 tm 表示的时间信息 //函数返回:以结构 tm 表示的时间信息指针 //用法: //参数说明: t 函数用 time()得到的时间信息 #include <stdio.h> #include <time.h> #include <windows.h> int main(void) { char *tzstr = "TZ = PST8PDT"; time_t t; struct tm *gmt, *area; putenv(tzstr); tzset(); time(&t); area = localtime(&t); printf("当地时间是: %s", asctime(area)); gmt = gmtime(&t); printf("格林尼治时间是: %s", asctime(gmt)); } 运行结果:

上个示例中提到 tzset():
//函数名称: tzset(); //函数原型:void __cdecl tzset(void) __MINGW_ATTRIB_DEPRECATED_MSVC2005; //函数功能:对UNIX操作系统的时间兼容性,用于得到时区 在 DOS 环境下无用途 //函数返回:无 //用法: #include <stdio.h> #include <time.h> #include <windows.h> int main(void) { time_t td; putenv("TZ = PST8PDT"); tzset(); time(&td); printf("当前时间 = %s", asctime(localtime(&td))); } 运行结果:

下面来介绍实现 自定义 时间格式输出函数:
//函数名称: strftime(); /*函数原型:size_t __cdecl strftime(char * __restrict__ _Buf,size_t _SizeInBytes,const char * __restrict__ _Format,const struct tm * __restrict__ _Tm); 它有4个参数: _Buf, 表示返回的时间字符串 _SizeInBytes, 要写入的字节的最大数量 _Format, 这是 C 字符串,包含了普通字符和特殊格式说明符的任何组合。 _Tm, 输入时间结构体 其中C字符串格式符说明如下: 说明符 替换为 示例 %a 缩写的星期几名称 Sun %A 完整的星期几名称 Sunday %b 缩写的月份名称 Mar %B 完整的月份名称 March %c 日期和时间表示法 Sun Jan 23 02:56:02 2022 %d 一月中的第几天(01-31) 19 %H 24 小时格式的小时(00-23) 14 %I 12 小时格式的小时(01-12) 05 %j 一年中的第几天(001-366) 231 %m 十进制数表示的月份(01-12) 08 %M 分(00-59) 55 %p AM 或 PM 名称 PM %S 秒(00-61) 02 %U 一年中的第几周,以第一个星期日作为第一周的第一天(00-53) 33 %w 十进制数表示的星期几,星期日表示为 0(0-6) 4 %W 一年中的第几周,以第一个星期一作为第一周的第一天(00-53) 34 %x 日期表示法 08/19/12 %X 时间表示法 02:50:06 %y 年份,最后两个数字(00-99) 01 %Y 年份 2012 %Z 时区的名称或缩写 CDT %% 一个 % 符号 % */ //函数功能:将时间结构体转换为指定的字符串格式 //函数返回:通过指定的字符串格式打印出来 //用法: #include <stdio.h> #include <time.h> int main(void) { time_t now_time; struct tm *info; char buffer[80]; time( &now_time ); info = localtime( &now_time ); strftime(buffer, 80, "%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S", info); printf("格式化的日期和时间 : %s n", buffer ); } 运行结果:

通过打印的结果可以看出,打印字符串的格式和函数中指定的字符串格式是一样的,这样通过对字符串格式的设置,就可按照自己的要求打印出时间和日期的字符串,使用起来更加灵活和方便。
关于 C 语言时间函数的用法和特色后续会在陆续补充





